Feed production lines
granulated and loose
Design and production of granulated feed production lines
Modern animal nutrition requires the use of safe and efficient technologies, which determine the price of livestock and the quality of meat. In this chain, Nawrocki Technologie Granulowania provides technological and technical solutions that guarantee the best production results for the producer and the feed and animals. Our experience includes the production of loose, sterilized and granulated feed.

The history of granulation in NPT dates back to the 1970s
Our adventure with feed pelleting technologies dates back to the 1970s, when the SPOMASZ Żnin Food Industry Machinery and Equipment Factory began producing GR2 305 granulators under a British license.
We have expanded the granulators with other devices for the production of granulated feeds in order to offer the emerging Polish feed market solutions that were the beginning of this industry.
From the beginning, we were the main designer of the technology, which was expanded to include sterilization, extrusion and other solutions that serve modern feed production.

Processes in the feed mixing plant
1. Receipt and cleaning of raw materials
A pitted hopper with a screw selector and a bucket elevator. The roofing with a canopy limits the inflow of unwanted elements. If necessary, we supply a hydraulic tipper.
When receiving wet raw materials, we use vacuum grain dryers.
The cleaner with filter ensures trouble-free and hygienic production of all feeds in the subsequent stages.
A system of hopper and flat-bottomed silos and storage tanks for storing main raw materials and additives.
2. Dosing and weighing
2.1. Micro Station
For precise dosing of bulk components.
Micro-dosing system consisting of stainless or acid-resistant steel tanks.
Highly accurate screw feeders precisely dose the specified portion of individual feed components. Equipped with pneumatic valves.
Square or round tanks with a capacity of 0.5m3 to 4m3 with Endress-Hauser or other level sensors.
The number of tanks is adapted to the recipe, usually from 6 to 30. The size of the tanks depends on the % share of the component. The material depends on the type of component, usually acid-resistant steel. Electronically secured hatches with a lock release from the central control system. Access to the hatches from a platform equipped with an electric crane with a lifting capacity of 3.2 tons.
In the case of difficult-to-flow raw materials, we use vibrators or hammers installed on the outlet cones.
The system is mounted on an independent structure.
Electronic cone scales for screw feeders with a capacity of 50, 100, 200 or 300 kg with pneumatic gate valves. Made of stainless steel.
2.2. Big bag station
Used for components such as lime, salt, etc.
Construction with a stainless steel sheet hopper and a screw feeder.
Connection to the scale using tarpaulin collars.
2.3. Manual unloading station
Made of acid-resistant steel with an emphasis on minimizing raw material residues.
Equipped with a receiving mechanism that minimizes dusting,
Independent dust filter with return to the transport system or with connection to a central filtration system.
The raw material tank is available in several volume variants.
Height adjustable.
Optional vibrator for more efficient emptying.
2.4. Macro weights
Tensometric scales, based on 3 sensors.
Individually tailored to the specific location and technological requirements.
Made of structural steel, on an independent structure with flexible connectors for screw feeders or other types of dosing systems. Possible execution in stainless steel.
Integrated discharge with quick auger selector, bolted and with seal. Adapted for connection to a bucket elevator.
2.5. Dosing of fats, acids, water, molasses
Dosage amount: 0.5% - 6%.
Realized from a tank (internal or external with heating) through insulated and heated pipelines with filters.
A set of pumps adapted to specific liquid raw materials.
Complete set of valves, pressure gauges, pumps and flow meters as well as a spray nozzle collector, signal and power wiring.
Nozzle assembly with automatic compressed air blowing.
Fully automated operation integrated with the central control system.
3. Grinding (grinding)
The process is carried out in horizontal or vertical beater mills or in grinders.
Machines with power adapted to the efficiency of the feed mill and the percentage of consumption of the given cereals.
The grinding unit consists of a magnetic separator, a buffer tank, a screw feeder, a grinder or mill, and a ground grain collection unit.
The local filter removes dust from the system and should be connected to a central dust removal system.
Possible integration of the grinding system with a mixing tank.
4. Mixing
Compact paddle mixers are a set used for effective and accurate (1:10,000 for feed) mixing of loose and liquid components intended for further processing (sterilization, granulation) or packaging and storage.
Capacities from 500l to 10,000 litres.
Mixing time: 6 minutes (10 batches per hour).
Equipped with a mixer tank, a mixer tank and a screw selector. Recommended for rooms with limited size.
Bomb-type dischargers with two flaps driven by pneumatic actuators.
Connector system with nozzles for dispensing fluids. Nozzles adapted to the type of fluid.
The construction of individual sections reduces the risk of any contamination to a minimum.
The special finish of the mixer's inner walls reduces the accumulation of residues from previous batches.
Mixing shaft blades made of acid-resistant steel.
5. Conditioning
It is an extremely important stage before sterilization and granulation of the loose mixture. It improves the digestibility and assimilation of feeds and has a huge impact on their high quality. In addition, the efficiency of granulation increases.
Conditioning is performed in one conditioner or a set of two extended-action conditioners, then the conditioning time is extended to up to 34 seconds.
The conditioner is made of acid-resistant steel, insulated with heating mats (optionally with an electric circuit), and has a steam connection with a manual shut-off valve.
The steam connection can be adapted to the existing steam reduction and stabilization unit.
6. Sterilization
Sterilization is an increasingly popular form of heat treatment of bulk feed mixtures, the purpose of which is to eliminate salmonella, bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms.
The process takes place immediately before pelleting in order to shorten the transport route and maintain a high feed temperature.
7. Granulation
It is a process of forming loose feed into granules of the required diameter and density.
In a granulator, two or three rollers press the feed into the holes of a die. This is where compression takes place and the granules are given a cylindrical shape.
8. Cooling of granulate
It is required to reduce moisture levels and increase the mechanical resistance of the granules.
9. Crushing the granulate
It takes place in roller crushers.
The aim is to break down the pellets into smaller fractions that can be consumed by the chicks.
Crushing is an alternative to microgranulation.
11. Greasing
The cooled and cleaned granules are sprayed with an additional dose of fat, which cannot be added at earlier stages.
The complete cold granule greasing system allows for increasing the calorific value of feed without reducing its mechanical properties, which are so important during storage and further transport.
10. Cleaning the granulate
The production process produces unwanted crumbs and dust that must be removed from the granulated mass before packaging, storage or shipping.
Vibrating screens are used for cleaning.
Click here to learn more about screeners >>
12. Packaging and palletizing
Granulate can be packed in bags. Weighing and packaging is fully automatic.
For capacities above 10 t/h, we recommend using a palletizer with a pallet wrapper in stretch film.
13. Storage and shipping
The finished granulated feed is transported via a horizontal and vertical transport system to silos and storage tanks, and from there to the packaging section or for truck dispatch.
14. Process automation
All machines, devices and supporting systems operate under the control of the AIAC automatic control system.
>> Plan of the bulk feed mixing plant and the feed pelleting line with dispatch
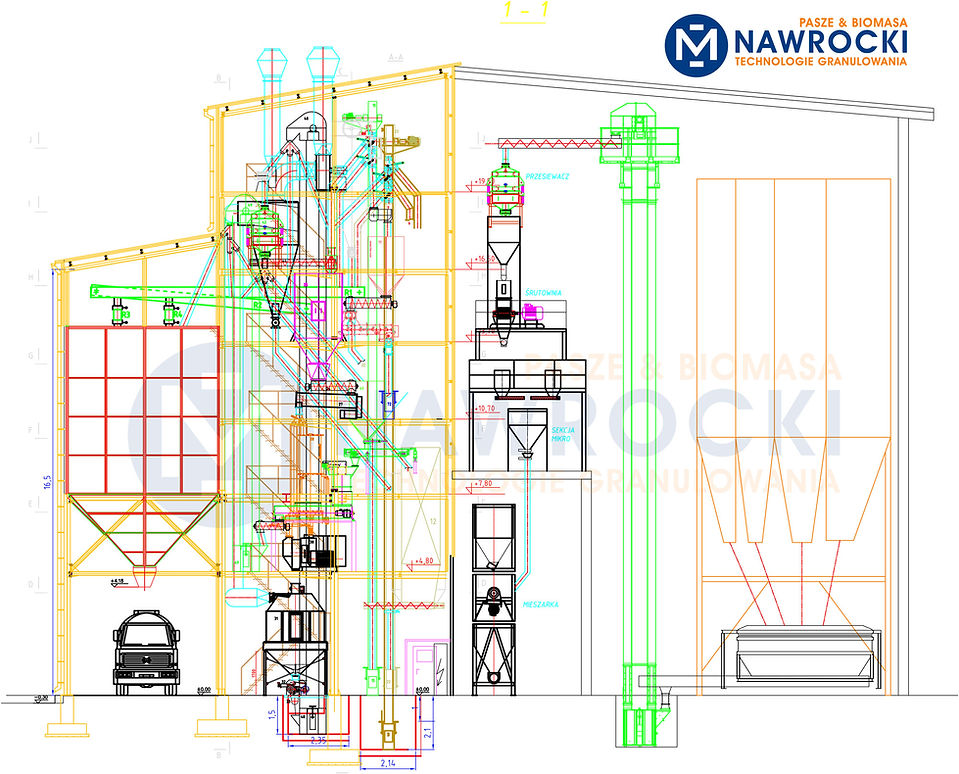
>> Plan of the feed pelleting line with the expedition

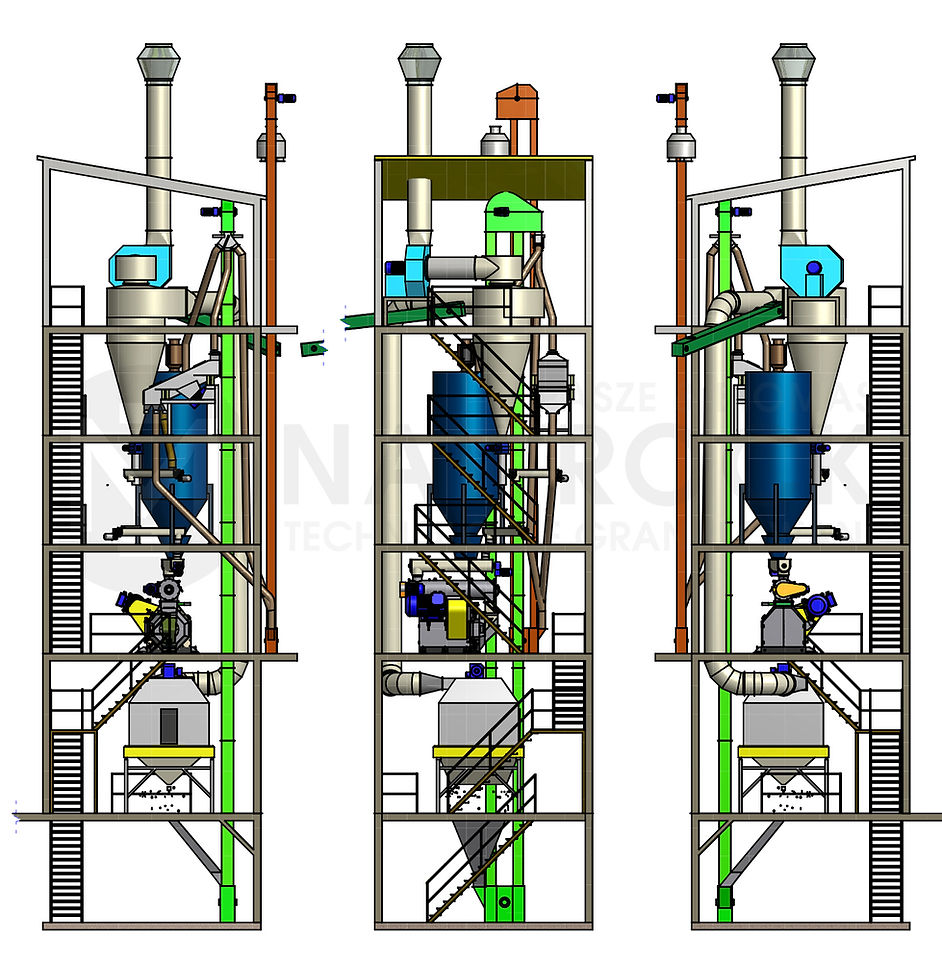
>> Projection of the vertical granulation line (gravity transport)
How are feed production technologies changing in the face of growing requirements from both producers and consumers? Technological innovations and growing expectations regarding the quality and safety of feed products require continuous improvement of production processes. In this context, NPT Nawrocki stands out in the industry by offering advanced lines for the production of granulated and loose feeds. Specializing in providing comprehensive solutions - from design to implementation - the company responds to dynamic changes in the feed industry by introducing innovations that raise the standards of efficiency and hygiene of production.
Granulated feed production lines
With the technological evolution, the production lines for granulated and loose feed offered by NPT Nawrocki have become an essential element ensuring efficiency, safety and innovation in feed production. The company with over 40 years of experience focuses on providing solutions tailored to individual customer needs - from design to comprehensive implementation of factories and production lines.
The technologies used by NPT Nawrocki cover a wide range of processes, such as granulation, sterilization or crushing. The specificity of feed production requires particular precision at each stage - from receiving raw materials, through their cleaning, dosing, mixing, to the final shaping and packaging of the final product. Each production line is designed with the aim of maximizing efficiency while minimizing the risk of contamination.
An example would be granulators, which are the most important element of the company's production lines. NPT Nawrocki designs granulators that not only effectively transform feed mass into granulate, but are also designed to meet expectations in terms of both efficiency and minimizing energy consumption.
The company is constantly investing in technological development, adapting its products to changing legal regulations and market needs. Thanks to this, NPT Nawrocki not only supplies production lines, but also acts as an advisor in the optimization of production processes in the feed industry.


